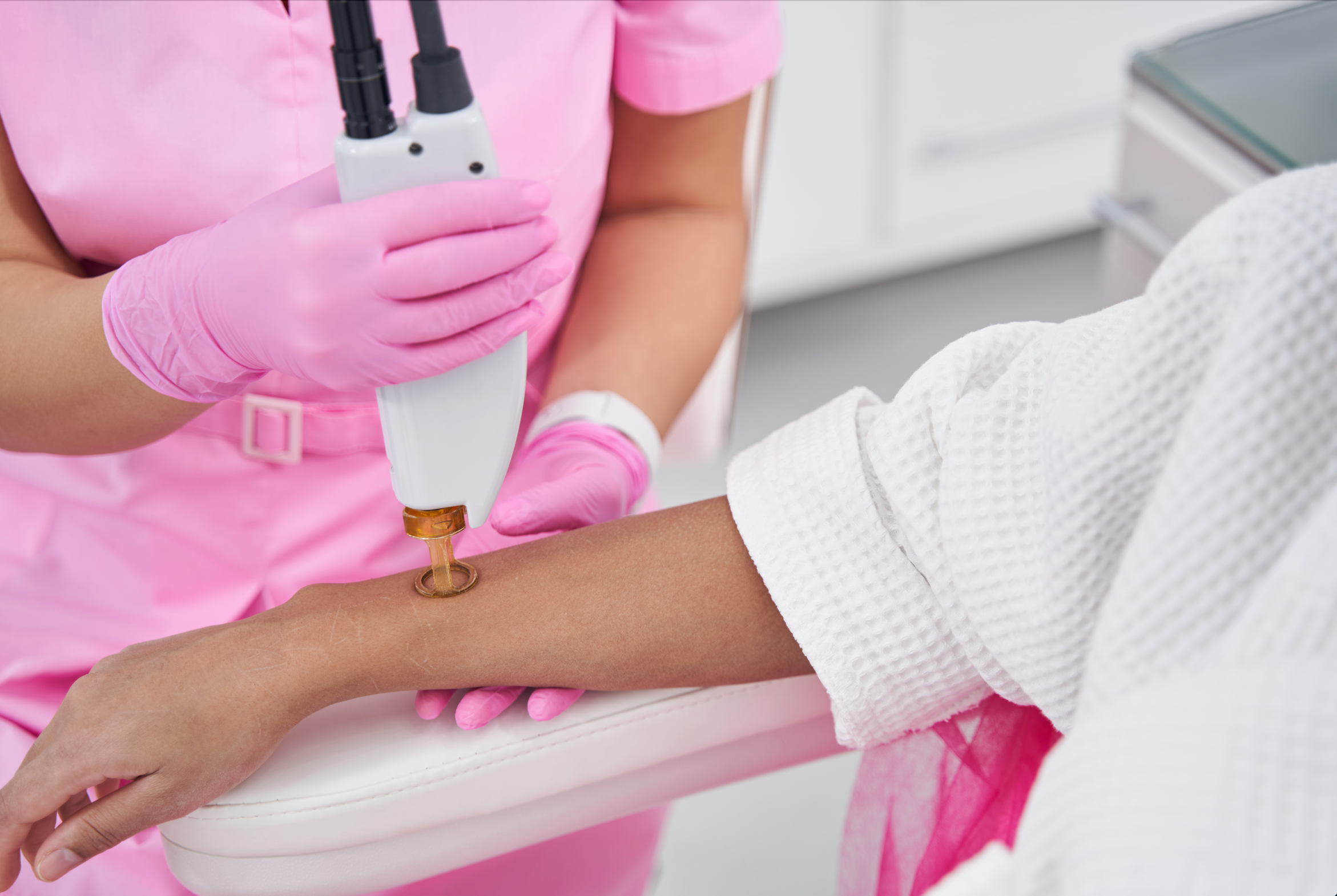
Unveiling the Science of Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal technology has revolutionised the aesthetic and medical industry by providing a lasting solution to unwanted hair. This blog post delves into the technology and science behind laser hair removal, aiming to give medical professionals a comprehensive understanding of the procedure, its applications, safety considerations, and the various technologies involved.
The Science
At the heart of laser hair removal is the principle of selective photothermolysis. This process targets the melanin in hair follicles, heating them to a point of destruction without damaging the surrounding tissue. The precision of selective photothermolysis ensures effective hair follicle destruction, making laser hair removal a preferred method for reducing unwanted hair growth.
The Technology
Understanding laser parameters for hair removal is crucial for optimising treatment outcomes. These parameters include the wavelength, pulse duration, and fluence (energy level) of the laser. The choice of parameters is influenced by the patient's skin type, hair colour, and hair thickness, as well as the specific laser device being used.
Melanin absorption in laser treatments plays a pivotal role in the efficacy of hair removal. Lasers are designed to emit wavelengths that are preferentially absorbed by the melanin in hair follicles. This absorption causes the follicles to heat up and ultimately be destroyed, preventing future hair growth.
Several types of laser devices are used for hair removal, each with its unique advantages:
Alexandrite laser for hair removal: Known for its efficacy in patients with light to olive skin tones, the Alexandrite laser operates at a 755 nm wavelength, offering a balance between melanin absorption and tissue penetration.
Diode laser hair removal: The Diode laser, with wavelengths around 810 nm, is versatile and effective on a broader range of skin types. It provides deeper penetration and can be adjusted for various hair types.
Nd:YAG laser technology: The Nd:YAG laser emits a 1064 nm wavelength, making it suitable for darker skin types. Its ability to reach deeper hair follicles with minimal melanin absorption makes it a safe choice for skin types IV to VI.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) hair removal: Although not a laser, IPL uses a broad spectrum of light to target melanin in the hair follicles. It's adaptable to different skin types and hair colours, but its efficacy can vary compared to dedicated lasers.
The Client Assessment
Laser treatment efficacy is influenced by the patient's skin type and hair characteristics. Skin type considerations in laser hair removal are critical; using the wrong laser type or settings can result in less effective treatments or adverse effects like burn, blister or scarring. Similarly, hair colour and thickness play a significant role in how well the laser targets the hair follicle.
The Safety Considerations
Laser hair removal safety is paramount. Adverse outcomes can be minimised through proper training, understanding of laser physics, and adherence to safety protocols. Potential side effects, such as temporary redness or pigmentation changes, are generally mild and can be mitigated with appropriate care.
Laser hair removal technology offers a sophisticated and effective solution for managing unwanted hair. By understanding the mechanisms, types of lasers, and considerations for different skin and hair types, medical professionals can optimise treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety. As this field continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements and research is essential for delivering high-quality care. To stay ahead and stay safe, come and do a laser hair removal course with us.
laser training, IPL, LLLT, laser safety course, laser safety training, laser online, laser safety officer certificate, laser safety officer, laser safety officers course, laser hair removal course, laser certificate, laser education, laser tattoo removal course, Brisbane, Queensland, Hobart, Tasmania, Perth, Western Australia, Sydney, NSW, Melbourne, Geelong, Victoria, Adelaide, South Australia, ACT, Canberra, accredited, endorsed, APHRA, CPD, nurse, nursing, laser IPL, doctor, medical, beauty therapist, dermal therapist, laser therapist, laser course, Sydney, Brisbane, Melbourne, laser safety course, low level laser, laser technician, podiatrist, podiatry, dentist, dentistry, physio, physiotherapist, laser course near me, laser course Brisbane, laser course Melbourne, laser course Sydney, laser course Perth, hospital, LSO, perioperative, theatre, surgical, operating suite, ARPANSA, ACORN, online, online course, accredited, endorsed, Laser Safety Committee, Workplace Health and Safety, low level laser therapy, laser tattoo removal, laser hair removal, laser pigmentation removal, RSO, radiation safety officer course, radiation safety officer.
Post Disclaimer
This blog post has been vigilantly researched and fact checked to ensure that it is accurate, reliable and up to date. You must keep in mind that errors and omissions may occur and that we welcome any feedback or corrections in this regard. We encourage you to do your own research to verify the accuracy and contemporary nature of the information presented.
